最近由于机缘巧合,结合最近工作中遇到的一些问题,深入了解了文件描述符(File Descriptor,简称FD,以下使用 FD 称谓)。预计会有两到三篇关于 FD 的文章陆续出来。首篇也就是这篇,作为基础篇,介绍一些关于通用 FD 的内容知识。
概念定义
- 文件描述符 是 用来访问资源(文件,输入输出设备等)的一种抽象指示符。
- 文件描述符 是POSIX(Portable Operating System Interface)规范的组成部分
- 文件描述符 通常是非负整数,C 语言中使用int类型。
FD 具体可以指向什么
- 文件/目录 files/directories
- 输入输出源 input/output
- 管道 pipes
- 套接字 sockets
- 其他 Unix 文件类型 other Unix files
系统默认的FDs
每一个 Unix 进程中,通常会有三个预制的 FD。它们分别是
- 标准输入 Standard input
- 标准输出 Standard output
- 标准错误(输出) Standard error
其对应的行为是
- 标准输入 用于程序接受数据
- 标准输出 用于程序输出数据
- 标准错误 用于程序输出错误或者诊断信息
内部机制
三张表
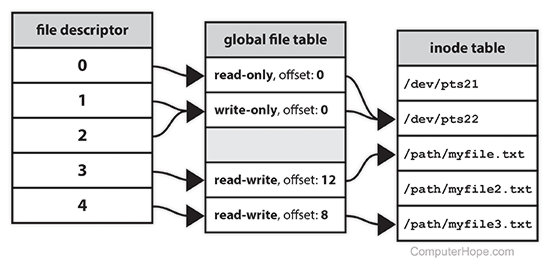
如上图从左至右有三张表
- file descriptor table 归属于单个进程
- global file table(又称open file table) 归属于系统全局
- inode table 归属于系统全局
从一次文件打开说起
当我们尝试打开文件/path/myfile.txt
1.从inode table 中查找到对应的文件节点
2.根据用户代码open的一些参数(比如读写权限等)在open file table 中创建open file 节点
3.将上一步的open file节点信息保存,在file descriptor table中创建 file descriptor
4.返回上一步的file descriptor的索引位置,供应用读写等使用。
备注:上述图片来自https://www.computerhope.com/jargon/f/file-descriptor.htm
FD 数量限制
出于稳定系统性能和避免因为过多打开文件导致CPU和RAM占用居高的考虑,系统都会设置了一个最大可用的 FD 数量。
FD上限值通常不小,一般应用很难达到。
限制类型
- hard limit 由系统管理权限人员设定,是soft limit 可以设置的上限
- soft limit 当前用户设置,用来限定进程,通常小于(但不能超过)hard limit值。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 | |
Questions
进程退出与 FD 关系
因为file descriptor table 存在于 PCB (进程控制块,Process Control Block) 中,进程退出后所有的 FD都需要关闭处理掉。
如下为POSIX文档
All of the file descriptors, directory streams, conversion descriptors, and message catalog descriptors open in the calling process shall be closed.
同一路径 与 FD 关系
- 同一文件,多次打开,FD值不同
- 同一文件,读写模式不同打开,FD值也不同
打开文件过多会怎样
open返回值会出现-1- 通常会导致进程无法进行,甚至是崩溃
示例验证代码
如下代码可以验证上述问题中的结论
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 | |
P.S.很多年不写C代码了。
References
- https://unix.stackexchange.com/questions/430365/what-happens-to-file-descriptors-when-the-process-is-killed
- https://apple.lib.utah.edu/open-file-limits-on-os-x-what-they-are-why-increase-them-and-how-to-increase-them/
- http://geekswing.com/geek/quickie-tutorial-ulimit-soft-limits-hard-limits-soft-stack-hard-stack/
- https://cseweb.ucsd.edu/classes/sp16/cse120-a/applications/ln/lecture15.html
- http://pubs.opengroup.org/onlinepubs/9699919799/functions/_Exit.html#tag_16_01_03_01
- File Descriptors Explained

