在Android开发中,View是我们必须要接触的用来展示的技术.通常情况下随着View视图的越来越复杂,整体布局的性能也会随之下降.这里介绍一个在某些场景下提升布局性能的View,它就是ViewStub.
ViewStub是什么
ViewStub是View的子类
它不可见,大小为0
用来延迟加载布局资源
注,关于Stub的解释
A stub is a small program routine that substitutes for a longer program, possibly to be loaded later or that is located remotely
在Java中,桩是指用来代替关联代码或者未实现代码的代码.
ViewStub使用场景
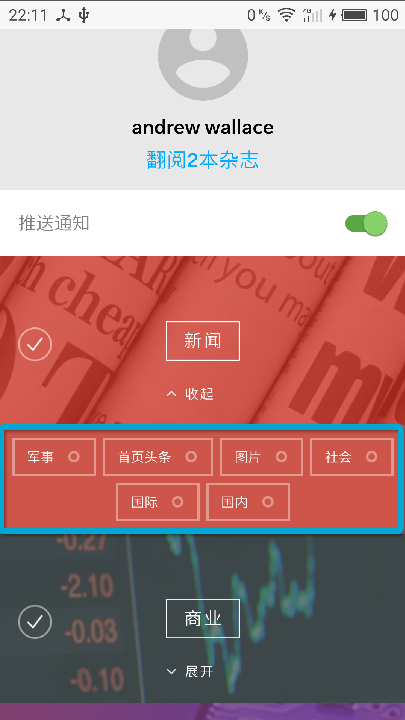
如上图所示,
一个ListView包含了诸如新闻,商业,科技等Item
每个Item又包含了各自对应的子话题,
但是子话题的View(蓝色区域)只有在点击展开按钮才真正需要加载.
如果默认加载子话题的View,则会造成内存的占用和CPU的消耗
所以,这时候就ViewStub就派上用处了.使用ViewStub可以延迟加载布局资源.
ViewStub 怎么用
在布局文件中使用ViewStub标签
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:paddingLeft="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"
android:paddingRight="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"
android:paddingTop="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin"
android:paddingBottom="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin"
tools:context="com.droidyue.viewstubsample.MainActivity">
<Button
android:id="@+id/clickMe"
android:text="Hello World!"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"/>
<ViewStub
android:id="@+id/myViewStub"
android:inflatedId="@+id/myInflatedViewId"
android:layout="@layout/include_merge"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_below="@id/clickMe"
/>
</RelativeLayout>
2.在代码中inflate布局
1
2
3
4
5
6
ViewStub myViewStub = ( ViewStub ) findViewById ( R . id . myViewStub );
if ( myViewStub != null ) {
myViewStub . inflate ();
//或者是下面的形式加载
//myViewStub.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
}
关于ViewStub的事
除了inflate方法外,我们还可以调用setVisibility()方法加载布局文件
一旦加载布局完成后,ViewStub会从当前布局层级中删除
android:id指定ViewStub ID,用于查找ViewStub进行延迟加载android:layout延迟加载布局的资源idandroid:inflatedId加载的布局被重写的id,这里为RelativeLayout的id
ViewStub的不足
官方的文档中有这样一段描述
Note: One drawback of ViewStub is that it doesn’t currently support the tag in the layouts to be inflated.
意思是ViewStub不支持<merge>标签.
关于不支持<merge>标签的程度,我们进行一个简单的验证
验证一:直接标签
如下,我们有布局文件名为merge_layout.xml
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
< merge xmlns: android = "http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" >
< Button
android: layout_width = "fill_parent"
android: layout_height = "wrap_content"
android: text = "Yes" />
< Button
android: layout_width = "fill_parent"
android: layout_height = "wrap_content"
android: text = "No" />
</ merge >
替换对应的ViewStub的android:layout属性值之后,运行后(点击Button按钮)得到产生了如下的崩溃
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
E AndroidRuntime: android . view . InflateException : Binary XML file line # 1 : < merge /> can be used only with a valid ViewGroup root and attachToRoot = true
E AndroidRuntime: at android . view . LayoutInflater . inflate ( LayoutInflater . java : 551 )
E AndroidRuntime: at android . view . LayoutInflater . inflate ( LayoutInflater . java : 429 )
E AndroidRuntime: at android . view . ViewStub . inflate ( ViewStub . java : 259 )
E AndroidRuntime: at com . droidyue . viewstubsample . MainActivity $ 1 . onClick ( MainActivity . java : 20 )
E AndroidRuntime: at android . view . View . performClick ( View . java : 5697 )
E AndroidRuntime: at android . widget . TextView . performClick ( TextView . java : 10815 )
E AndroidRuntime: at android . view . View $PerformClick . run ( View . java : 22526 )
E AndroidRuntime: at android . os . Handler . handleCallback ( Handler . java : 739 )
E AndroidRuntime: at android . os . Handler . dispatchMessage ( Handler . java : 95 )
E AndroidRuntime: at android . os . Looper . loop ( Looper . java : 158 )
E AndroidRuntime: at android . app . ActivityThread . main ( ActivityThread . java : 7237 )
E AndroidRuntime: at java . lang . reflect . Method . invoke ( Native Method )
E AndroidRuntime: at com . android . internal . os . ZygoteInit $MethodAndArgsCaller . run ( ZygoteInit . java : 1230 )
E AndroidRuntime: at com . android . internal . os . ZygoteInit . main ( ZygoteInit . java : 1120 )
E AndroidRuntime: Caused by: android . view . InflateException : < merge /> can be used only with a valid ViewGroup root and attachToRoot = true
E AndroidRuntime: at android . view . LayoutInflater . inflate ( LayoutInflater . java : 491 )
E AndroidRuntime: ... 13 more
可见,直接的<merge>标签,ViewStub是不支持的.
验证二 间接的ViewStub
下面布局间接使用了merge标签.文件名为include_merge.xml
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
<? xml version = "1.0" encoding = "utf-8" ?>
< LinearLayout xmlns: android = "http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android: orientation = "vertical"
android: layout_width = "match_parent"
android: layout_height = "match_parent" >
< include layout = "@layout/merge_layout" />
</ LinearLayout >
然后修改ViewStub的android:layout值,运行,一切正常.
除此之外,本例也验证了ViewStub也是对<include>标签支持良好的.
关于ViewStub的一点代码剖析
inflate vs setVisibility
inflate和setVisibility的共同点是都可以实现加载布局
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
/**
* When visibility is set to {@link #VISIBLE} or {@link #INVISIBLE},
* {@link #inflate()} is invoked and this StubbedView is replaced in its parent
* by the inflated layout resource.
*
* @param visibility One of {@link #VISIBLE}, {@link #INVISIBLE}, or {@link #GONE}.
*
* @see #inflate()
*/
@Override
public void setVisibility ( int visibility ) {
if ( mInflatedViewRef != null ) {
View view = mInflatedViewRef . get ();
if ( view != null ) {
view . setVisibility ( visibility );
} else {
throw new IllegalStateException ( "setVisibility called on un-referenced view" );
}
} else {
super . setVisibility ( visibility );
if ( visibility == VISIBLE || visibility == INVISIBLE ) {
inflate ();
}
}
}
setVisibility只是在ViewStub第一次延迟初始化时,并且visibility是非GONE时,调用了inflate方法.
inflate源码
通过阅读下面的inflate方法实现,我们将更加理解
android:inflatedId的用途
ViewStub在初始化后从视图层级中移除
ViewStub的layoutParameters应用
mInflatedViewRef通过弱引用形式,建立ViewStub与加载的View的联系.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
/**
* Inflates the layout resource identified by {@link #getLayoutResource()}
* and replaces this StubbedView in its parent by the inflated layout resource.
*
* @return The inflated layout resource.
*
*/
public View inflate () {
final ViewParent viewParent = getParent ();
if ( viewParent != null && viewParent instanceof ViewGroup ) {
if ( mLayoutResource != 0 ) {
final ViewGroup parent = ( ViewGroup ) viewParent ;
final LayoutInflater factory = LayoutInflater . from ( mContext );
final View view = factory . inflate ( mLayoutResource , parent ,
false );
if ( mInflatedId != NO_ID ) {
view . setId ( mInflatedId );
}
final int index = parent . indexOfChild ( this );
parent . removeViewInLayout ( this );
final ViewGroup . LayoutParams layoutParams = getLayoutParams ();
if ( layoutParams != null ) {
parent . addView ( view , index , layoutParams );
} else {
parent . addView ( view , index );
}
mInflatedViewRef = new WeakReference < View >( view );
if ( mInflateListener != null ) {
mInflateListener . onInflate ( this , view );
}
return view ;
} else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException ( "ViewStub must have a valid layoutResource" );
}
} else {
throw new IllegalStateException ( "ViewStub must have a non-null ViewGroup viewParent" );
}
}
关于ViewStub的研究就是这些,希望对大家关于优化视图有所帮助和启发.